Down Syndrome
History
The discovery of Down syndrome was made by Dr. John Langdon Down in 1866. He was the first to realise that a large number of his patients looked very similar in physical features. At the time, he called them "Mongoloids" but in the year 1960 there was an uproar of disgusted Mongolians. They forced the name to be changed. It was later altered to Down's syndrome in honour of John Langdon Down; in North America it is known as just Down syndrome. In 1959 Dr. Jérôme Lejeune learned that the source of Down syndrome was from a third chromosome on the 21st pair. Dr. Lejeune later called it Trisomy 21 although it is much less common than the name Down syndrome.
Symptoms
Individuals with Down syndrome have a certain set of physical features that make them very distinctive. It can cause mild to moderate development disabilities for victims. A small number of these individuals have severe to profound mental disability. Down syndrome is fairly common; about 1 in 800 to 1,000 births are affected by it. Symptoms of the syndrome can be on varying levels of degree. Some of these common features include:
- An abnormally small chin
- An oversized tongue
- Almond shaped eyes
- Shorter limbs with poor muscle tone
- A single crease in the palm of their hand
- A larger space between the big and second toe
- Congenital heart defects (defect in structure of heart)
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (chronic symptoms cause damage due to abnormal reflux in the esophagus)
- Recurrent ear infections
- Obstructive sleep apnea (a breathing disorder that occurs during sleep)
- Thyroid dysfunctions
Treatment
Treatment for those with Down syndrome is used to focus on controlling the symptoms and health concerns but not the actual syndrome. Some of the treatments can be very simple like regular checkups and screening to check on progress of everything. Medications and surgery can be used to help correct symptoms and other major problems that occur along with Down syndrome. Counseling and other forms of support are available for individuals that may encounter tough times through their life.
Prognosis
Health complications and symptoms can contribute to the lifespan of someone living with Down syndrome. A study that took place in America in 2002 had shown that the average lifespan of someone living with Down syndrome is around 49 years of age. The study had shown a significant differential between statistics with another study done in 1980, which had the average lifespan at 25 years during that time. As age increases, more health problems occur as well; an Alzheimer's-like disease is common in those nearing the end of their life between their 40's and 50's.
Karyotype
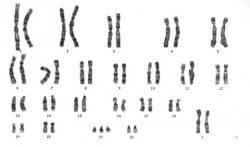
This picture (left) shows the karyotype of a female with Down syndrome. On the 21st pair, there is an extra chromosome attached to the other two which is causing this particular type of syndrome to occur.
Albinism
History
Sir Archibald Garrod made the discovery of Albinism in 1908, even though previous scholars had observed the disease. Other names for Albinism include: achromia, achromasia, and achromatosis all of which come from the Latin word albus, meaning white. Albinism is a form of hypopigmentary disorder that a person is born with, caused by the shortage or complete absence of melanin pigment. The lack of pigment causes a deficiency of colour in the eyes, skin, and hair, normally making these parts white. Altered genes are the result of Albinism, and in many cases the disease is passed down from parents.
Symptoms
Albinism is not an infectious disease and consequently cannot be passed on through contact or blood transfusions. On average, about 1 in 17,000 people are affected by Albinism. Symptoms of those with Albinism is contingent to the particular kind of Albinism one may have. Albinism can only affect the eyes, skin, and hair, and therefore, the different kinds can affect an assortment of these body parts.
Symptoms for the eye can include:
Symptoms for the eye can include:
- Lazy eye
- Wandering eye
- Sensitivity to bright lights
- Poor vision
- Red eyes
- Portion of hair turning white
- Complete whiteness of hair
- Extremely pale or entire whiteness of skin
- Patches of white skin
- Greater vulnerability to sunburn
- Highly prone to skin cancer
Treatment
At this point in time, there has been no found cure, instead, treatment is targeted at reducing or preventing the effects of the symptoms. Protection from the sun is a great way to start on prevention: wearing sunglasses, long sleeves, and sunscreen with high SPF, and avoiding the sun altogether. Surgery or certain eyewear (glasses or contacts) can reverse the effects that symptoms have on the eyes. For skin, surgery to take out or cure skin cancer can be done. Studies on Albino mice have been done to see how treatments may affect humans.
Prognosis
Those living with Albinism have a lifespan similar to that of a healthy human, that is, if no other health problems come up. Albinos have an increased chance of cancer which can easily affect the length of life for patients. Albinism doesn't cause any mental disabilities or growth problems th them grow like anyone else.
Albino Child
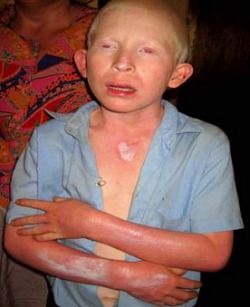
This picture (left) has an Albino child with all the examples of someone living with Albinism. The child has white hair, and skin as well as red eyes.
Bibliography
- 20, the. "Down syndrome - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia." Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Nov. 2009. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Down_syndrome>.
- "A History of Down Syndrome." Scared Of Down Syndrome? Don't Be. What You Need To Know, Now. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2009. <http://www.down-syndrome-facts-and-fiction.com/history-of-down-syndrome.html>.
- "Albinism - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia." Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 25 Nov. 2009. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Albinism>.
- "Down Syndrome." Down Syndrome Home Page. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2009. <http://down-syndrome.emedtv.com/down-syndrome/down-syndrome.html>.
- "Who Discovered Albinism | Wooden Spears." Hollywood Celebrity Gossip Blog| Britney Spears Gossip| Paris Hilton News| Lindsay Lohan Gossip| Zac Efron. N.p., n.d. Web. 25 Nov. 2009. <http://woodenspears.com/who-discovered-albinism/>.
- "Your Health - Albinism." Aurora Health Care - Wisconsin hospitals, doctors and clinics . N.p., n.d. Web. 25 Nov. 2009. <http://www.aurorahealthcare.org/yourhealth/healthgate/getcontent.asp?URLhealthgate=%2222573.html%22>.
